General Information
Bladder cancer is a disease in which malignant (cancer) cells form in the tissues of the bladder. The bladder is a hollow organ in the lower part of the abdomen. It is shaped like a small balloon and has a muscular wall that allows it to get larger or smaller. The bladder stores urine until it is passed out of the body.
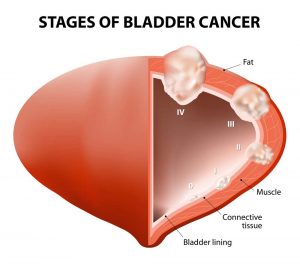 Urine is the liquid waste that is made by the kidneys when they clean the blood. The urine passes from the two kidneys into the bladder through two tubes called ureters. When the bladder is emptied during urination, the urine goes from the bladder to the outside of the body through another tube called the urethra. These and other symptoms may be caused by bladder cancer.
Urine is the liquid waste that is made by the kidneys when they clean the blood. The urine passes from the two kidneys into the bladder through two tubes called ureters. When the bladder is emptied during urination, the urine goes from the bladder to the outside of the body through another tube called the urethra. These and other symptoms may be caused by bladder cancer.
However, a proper diagnosis is needed as other conditions may cause the same symptoms as bladder cancer.
General Information
Bladder cancer is a disease in which malignant (cancer) cells form in the tissues of the bladder. The bladder is a hollow organ in the lower part of the abdomen. It is shaped like a small balloon and has a muscular wall that allows it to get larger or smaller. The bladder stores urine until it is passed out of the body.
 Urine is the liquid waste that is made by the kidneys when they clean the blood. The urine passes from the two kidneys into the bladder through two tubes called ureters. When the bladder is emptied during urination, the urine goes from the bladder to the outside of the body through another tube called the urethra. These and other symptoms may be caused by bladder cancer.
Urine is the liquid waste that is made by the kidneys when they clean the blood. The urine passes from the two kidneys into the bladder through two tubes called ureters. When the bladder is emptied during urination, the urine goes from the bladder to the outside of the body through another tube called the urethra. These and other symptoms may be caused by bladder cancer.
However, a proper diagnosis is needed as other conditions may cause the same symptoms as bladder cancer.
Symptoms
A doctor should be consulted immediately if any of the following problems occur:
- Blood in the urine (slightly rusty to bright red in color).
- Frequent urination, or feeling the need to urinate without being able to do so.
- Pain during urination.
- Lower back pain.
Bladder Cancer Testing
CT scan (CAT scan)
A procedure that makes a series of detailed pictures of areas inside the body, taken from different angles. The pictures are made by a computer linked to an x-ray machine. A dye may be injected into a vein or swallowed to help the organs or tissues show up more clearly. This procedure is also called computed tomography, computerized tomography, or computerized axial tomography.
Urinalysis
A test to check the color of urine and its contents, such as sugar, protein, red blood cells, and white blood cells.
Internal exam: An exam of the vagina and/or rectum. The doctor inserts gloved fingers into the vagina and/or rectum to feel for lumps.
Intravenous pyelogram (IVP)
A series of x-rays of the kidneys, ureters, and bladder to find out if cancer is present in these organs. A contrast dye is injected into a vein. As the contrast dye moves through the kidneys, ureters, and bladder, x-rays are taken to see if there are any blockages.
Cystoscopy
A procedure to look inside the bladder and urethra to check for abnormal areas. A cystoscope is inserted through the urethra into the bladder. A cystoscope is a thin, tube-like instrument with a light and a lens for viewing. It may also have a tool to remove tissue samples, which are checked under a microscope for signs of cancer.
Biopsy
The removal of cells or tissues so they can be viewed under a microscope by a pathologist to check for signs of cancer. A biopsy for bladder cancer is usually done during cystoscopy. It may be possible to remove the entire tumor during biopsy.
Urine cytology
Examination of urine under a microscope to check for abnormal cells.
